The Sharp GP2Dxxx family is often used in robotics as distance sensors because the sensors are cheap and everywhere available. The normal use of these sensors is for the automatic flush of a restroom urinal or automatic air dryers, not for robotics.

The following sensors with analog output exists:
- Sharp GP2Y0A02YK has a range from 20..150cm
- Sharp GP2D12 (replaced by GP2YA21YK) has a range from 10..80cm
- Sharp GP2D120 has a range fro 4..30cm
Using analog sensors in robotic environment isn’t as easy as it’s seems. When you attach the Sharp sensor output to an oscilloscope you’ll see a noisy signal with a lot of spikes.
Solution
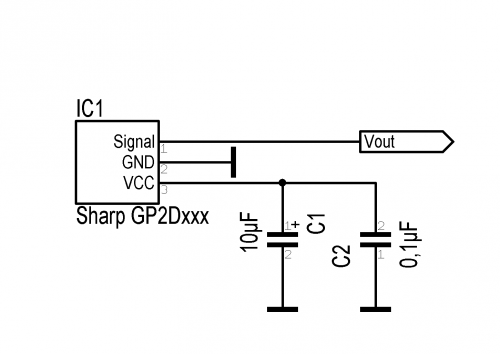
The solution for this problem is really simple. Add a capacitor of 100nF between VCC and GND to eliminate the spikes. A second capacitor of 10..100µF will eliminate most of the bounces from the output signal. The capacitors must be connected as close as possible on the sensor. The following pictures shows a solution with SMD capacitors.
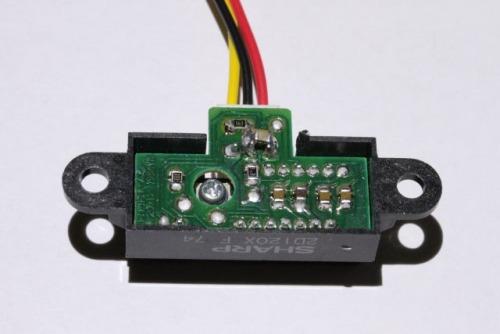
The Schematic for this modification is shown here:
Video
The following video shows the output signal of a Sharp GP2D120 sensor on an oscilloscope. First the signal of an unmodified sensor is shown, than the same sensor after the modification.
More Tips
- The housing of the Sharp sensors is conductive. If your robot has a metallic chassis, you should isolate the housing from the chassis.
- The output signal of the sensor isn’t linear. Especially at a closer distance, closer than the specific sensor minimum , you can’t get any useful signal.
