RFID Reader am Arduino: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „== Anschluss des RFID-RC522 an den Arduino == zum Anschluss des RFID-RC522 RFID Moduls an ein Arduino Board werden die 5 I/Os benötigt, die SPI I/Os SS;S…“) |
(kein Unterschied)
|
Version vom 10. Mai 2018, 11:41 Uhr
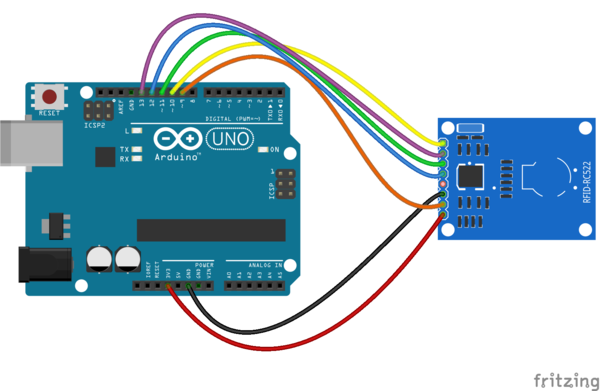
Anschluss des RFID-RC522 an den Arduino
zum Anschluss des RFID-RC522 RFID Moduls an ein Arduino Board werden die 5 I/Os benötigt, die SPI I/Os SS;SCK;MOSI MISO und ein Rest Pin.
Programm für den Arduino
Das Arduino Programm initialisiert das RFID Modul und gibt Information des RFID Chip über die serielle Schnittstelle aus.
<syntaxhighlight lang="Arduino">
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- * Example sketch/program showing how to read data from a PICC to serial. * ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- * This is a MFRC522 library example; for further details and other examples see: https://github.com/miguelbalboa/rfid * * Example sketch/program showing how to read data from a PICC (that is: a RFID Tag or Card) using a MFRC522 based RFID * Reader on the Arduino SPI interface. * * When the Arduino and the MFRC522 module are connected (see the pin layout below), load this sketch into Arduino IDE * then verify/compile and upload it. To see the output: use Tools, Serial Monitor of the IDE (hit Ctrl+Shft+M). When * you present a PICC (that is: a RFID Tag or Card) at reading distance of the MFRC522 Reader/PCD, the serial output * will show the ID/UID, type and any data blocks it can read. Note: you may see "Timeout in communication" messages * when removing the PICC from reading distance too early. * * If your reader supports it, this sketch/program will read all the PICCs presented (that is: multiple tag reading). * So if you stack two or more PICCs on top of each other and present them to the reader, it will first output all * details of the first and then the next PICC. Note that this may take some time as all data blocks are dumped, so * keep the PICCs at reading distance until complete. * * @license Released into the public domain. * * Typical pin layout used: * ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- * MFRC522 Arduino Arduino Arduino Arduino Arduino * Reader/PCD Uno/101 Mega Nano v3 Leonardo/Micro Pro Micro * Signal Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin * ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- * RST/Reset RST 9 5 D9 RESET/ICSP-5 RST * SPI SS SDA(SS) 10 53 D10 10 10 * SPI MOSI MOSI 11 / ICSP-4 51 D11 ICSP-4 16 * SPI MISO MISO 12 / ICSP-1 50 D12 ICSP-1 14 * SPI SCK SCK 13 / ICSP-3 52 D13 ICSP-3 15 */
- include <SPI.h>
- include <MFRC522.h>
- define RST_PIN 9 // Configurable, see typical pin layout above
- define SS_PIN 10 // Configurable, see typical pin layout above
MFRC522 mfrc522(SS_PIN, RST_PIN); // Create MFRC522 instance
void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communications with the PC while (!Serial); // Do nothing if no serial port is opened (added for Arduinos based on ATMEGA32U4) SPI.begin(); // Init SPI bus mfrc522.PCD_Init(); // Init MFRC522 mfrc522.PCD_DumpVersionToSerial(); // Show details of PCD - MFRC522 Card Reader details Serial.println(F("Scan PICC to see UID, SAK, type, and data blocks...")); }
void loop() { // Look for new cards if ( ! mfrc522.PICC_IsNewCardPresent()) { return; }
// Select one of the cards if ( ! mfrc522.PICC_ReadCardSerial()) { return; }
// Dump debug info about the card; PICC_HaltA() is automatically called mfrc522.PICC_DumpToSerial(&(mfrc522.uid)); }